
近几天,新冠疫情又在国内局部地区卷土重来,广东省等抗疫工作开始严峻。而作为每一个公民,我们首先要做好个人防疫,增强自身免疫力,尤其要控制体重,注意代谢问题。今天我们来看看国际上对于肥胖、代谢健康受损和新冠之间联系的认知。
参考文献
来源:《自然》期刊 2021-1-21
Global pandemics interconnected — obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19
全球流行病相互关联——肥胖、代谢健康受损和 COVID-19
作者:
Norbert Stefan,
Andreas L. Birkenfeld
Matthias B. Schulze

Obesity and impaired metabolic health are established risk factors for the non-communicable diseases (NCDs) type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative diseases, cancer and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, otherwise known as metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). With the worldwide spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), obesity and impaired metabolic health also emerged as important determinants of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, novel findings indicate that specifically visceral obesity and characteristics of impaired metabolic health such as hyperglycaemia, hypertension and subclinical inflammation are associated with a high risk of severe COVID-19. In this Review, we highlight how obesity and impaired metabolic health increase complications and mortality in COVID-19. We also summarize the consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection for organ function and risk of NCDs. In addition, we discuss data indicating that the COVID-19 pandemic could have serious consequences for the obesity epidemic. As obesity and impaired metabolic health are both accelerators and consequences of severe COVID-19, and might adversely influence the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines, we propose strategies for the prevention and treatment of obesity and impaired metabolic health on a clinical and population level, particularly while the COVID-19 pandemic is present.

概要:
一、肥胖和代谢健康受损是非传染性疾病 (NCD) 2 型糖尿病、心血管疾病、神经退行性疾病、癌症和非酒精性脂肪肝,也称为代谢相关脂肪肝 (MAFLD) 的既定风险因素。
二、随着严重急性呼吸系统综合症冠状病毒 2 (SARS-CoV-2) 在全球范围内的传播,肥胖和代谢健康受损也成为 严重冠状病毒病 (COVID-19) 的重要决定因素。
三、新发现表明,特别是内脏肥胖和代谢健康受损的特征,如高血糖、高血压和亚临床炎症,与严重 COVID-19 的高风险有关。
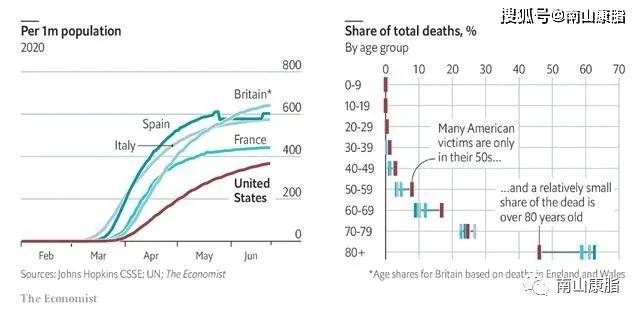
在这篇综述中,我们强调了肥胖和代谢健康受损如何增加 COVID-19 的并发症和死亡率。
我们还总结了 SARS-CoV-2 感染对器官功能和非传染性疾病风险的影响。
此外,我们讨论了表明 COVID-19 大流行可能对肥胖流行产生严重后果的数据。
由于肥胖和代谢健康受损都是严重 COVID-19 的加速器和后果,并可能对 COVID-19 疫苗的功效产生不利影响,我们提出了在临床和人群水平上预防和治疗肥胖和代谢健康受损的策略,特别是在 COVID-19 大流行期间。
Obesity, particularly severe obesity, is a strong and independent determinant of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); novel studies also suggest that visceral obesity increases the risk of complications.
·
Although diabetes mellitus is an established risk factor for severe COVID-19, evidence is increasing that hyperglycaemia in the non-diabetic and diabetic range also strongly predicts severe COVID-19.
·
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) targets organs and tissues that are relevant for cardiometabolic health; SARS-CoV-2-induced organ or tissue dysfunction could result in an increased incidence of cardiometabolic diseases.
·
Targeted interventions for metabolic pathologies could improve management of COVID-19; the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination response should be carefully evaluated in patients with obesity and/or diabetes mellitus because of a potentially reduced response.
·
Programmes resulting in weight loss and the improvement of metabolic health in people with metabolically unhealthy obesity should be implemented at the patient level and in the public health sector.
·
Research to understand how diet and nutritional status modify the immune response could help explain some of the variability in COVID-19 morbidity and mortality and improve patient outcomes.

主要结论:
一、肥胖,尤其是重度肥胖,是严重冠状病毒病 (COVID-19) 的强大且独立的决定因素。
二、新的研究还表明,内脏肥胖会增加并发症的风险。
尽管糖尿病是严重 COVID-19 的既定危险因素,但越来越多的证据表明,非糖尿病和糖尿病范围内的高血糖也强烈预示着严重的COVID-19。
严重急性呼吸系统综合症冠状病毒 2 (SARS-CoV-2) 靶向与心脏代谢健康相关的器官和组织;SARS-CoV-2 引起的器官或组织功能障碍可能导致心脏代谢疾病的发病率增加。
针对代谢病理的有针对性的干预措施可以改善 COVID-19 的管理;应仔细评估肥胖和/或糖尿病患者的 SARS-CoV-2 疫苗接种反应,因为可能会降低反应。
应在患者层面和公共卫生部门实施导致代谢不健康肥胖患者体重减轻和代谢健康改善的计划。
了解饮食和营养状况如何改变免疫反应的研究有助于解释 COVID-19 发病率和死亡率的一些变异性,并改善患者的预后。
所以要从根本上解决肥胖和代谢问题。






